python中\
两个反斜杠在r模式下才等于一个反斜杠
t = '03\\01\\2016'
print(t) # 03\01\2016
t == '03\01\2016' # False
text1 = '03\\01\\2016'
import re
if re.match(r'\d+\\\d+\\\d+',text1):
print('yes')
else:
print('no')
# 输出:yes
常用内置函数
reduce
- reduce(function, sequence, starting_value)
对sequence中的item顺序迭代调用function,如果有starting_value,还可以作为初始值调用. 例如可以用来对List求和:
def add(x,y): return x + y
reduce(add, range(1, 11))
# 结果:55 (注:1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10)
reduce(add, range(1, 11), 20)
# 结果:75 (注:20+1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10)
filter
- filter(function, sequence)
对sequence中的item依次执行function(item),将执行结果为True的item组成一个List/String/Tuple(取决于sequence的类型)
map
- map(function, sequence)
对sequence中的item依次执行function(item),见执行结果组成一个List返回
API
API 接口属于一种操作系统或程序接口,GUI接口属于一种图形操作系统。
两者都属于直接用户接口。有时公司会将 API 作为其公共开放系统。也就是说,公司制定自己的系统接口标准,当需要执行系统整合、自定义和程序应用等操作时,公司所有成员都可以通过该接口标准调用源代码,该接口标准被称之为开放式API。
- api:没有页面、没有状态
在python中弹出窗口提示
return HttpResponse('<html><script type="text/javascript">alert("已经填写过数据"); '
'window.location="setup"</script></html>')
JSON
JSON只是一种数据交换格式。JSON和XML是同一类东西。json.loads是将字符串里描述的JSON对象反序列化为Python对象
json.dumps() # 把字典、列表序列化成字符串
json.loads() # 把字符串反序列化成字典、列表
data = {'a':123, 'b':[1,2 ]}
d1 = json.dumps(data)
type(data) # <class 'dict'>
type(d1) # <class 'str'>
d2 = json.loads(d1)
type(d2) # <class 'dict'>
查看库版本
xx.version
xx.__version__
xx.getVersion()
input输入
python3中
- 只有input输入
python2中
- input输入数字
- raw_input输入字符串
nodejs升级
sudo npm cache clean -f
sudo npm install -g n
sudo n stable
raml建模语言
sudo npm i -g raml2html
raml2html --help
raml2html example.raml > example.html
raml2html -t examples/custom-template-test/template.nunjucks -i example.raml -o example.html
# 更新raml文档
cd api-raml-doc
raml2html raml/api.raml > index.html
format格式化代码输出
- 两个return 等价
def __repr__(self):
# !r 格式化代码,格式化代码 {0.x} 对应的是第1个参数的x属性
return 'Pair({0.x!r}, {0.y!r})'.format(self)
# return 'Pair(%r, %r)' % (self.x, self.y)
# 'The value is {:0,.2f},other value {}'.format(x, 23)
# 'The value is 1,234.57,other value 23'
文件写入
你想像一个文件中写入数据,但是前提必须是这个文件在文件系统上不存在。 也就是不允许覆盖已存在的文件内容。
解决方案:可以在 open() 函数中使用 x 模式来代替 w 模式的方法来解决这个问题。
with open('somefile', 'xt') as f:
f.write('Hello\n')
with open('test.txt', 'rt') as f:
data = f.read()
# 读取的是home目录下的test.txt文件
# wt:为了写入一个文本文件,使用带有 wt 模式的 open() 函数, 如果之前文件内容存在则清除并覆盖掉。
# rt:使用带有 rt 模式的 open() 函数读取文本文件。
# at:如果是在已存在文件中添加内容,使用模式为 at 的 open() 函数。
查看系统文件的读写操作默认使用编码
import sys
sys.getdefaultencoding()
火狐浏览器插件
- HttpRequester
- RESTClient
- Ubuntu Modifications
range
L = range(1,101)
L[:10:2] # 前10个数,每两个取一个
L[1::2] # 从下标1开始,每两个取一个
sqlite3安装失败原因
pyenv 环境中的python要重新安装
- 解决方法
sudo rm /usr/bin/python
sudo ln -s /usr/include/python3.2 /usr/bin/python
- 查询表结构
select * from sqlite_master where type="table" and name="xx";
print()禁止换行
可以使用在 print() 函数中使用 sep 和 end关键字参数,以你想要的方式输出。比如:
print('ACME', 50, 91.5) # ACME 50 91.5
print('ACME', 50, 91.5, sep=',') # ACME,50,91.5
print('ACME', 50, 91.5, sep=',', end='!!\n') # ACME,50,91.5!!
# 使用 end 参数也可以在输出中禁止换行,或者在print()后面加个逗号(但这样就会多了一个逗号,可以用\b退格把逗号删除)。比如:
for i in range(5):
print(i, end=' ') # 0 1 2 3 4
row = ('ACME', 50, 91.5)
print(row, sep='-') # ('ACME', 50, 91.5)
print(*row, sep='-') # ACME-50-91.5
根据依赖文件安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
missing
# __missing__() 方法可以让你定义如何处理缺失的值。
class safesub(dict):
"""防止key找不到"""
def __missing__(self, key):
return '{' + key + '}'
round
当一个值刚好在两个边界的中间的时候, round 函数返回离它最近的偶数。 也就是说,对1.5或者2.5的舍入运算都会得到2。
numpy
pip install numpy # [详细官网网址](http://www.numpy.org)
dateutil
pip install python-dateutil
加密
# key必须是16位
key = '0123456789abcdef'
mode = AES.MODE_CBC
iv = key
encryptor = AES.new(key, mode, iv)
# 要加密的内容必须是16位
text = 'hellohellohelloh'
# ase加密
ciphertext = encryptor.encrypt(text)
print(ciphertext)
# ase解密
decryptor = AES.new(key, mode, iv)
plain = decryptor.decrypt(ciphertext)
print(plain)
# md5加密(算法不可逆,所以不能解密)
import hashlib
# 创建md5对象
m = hashlib.md5()
# 生成加密串,其中qwertt是要加密的字符串
m.update(b"qwertt")
m.digest()
# 获取加密串
pwd = m.hexdigest()
print(pwd)
正则表达式匹配
import re
arr=re.findall(r"a(\d+)b.+a(\d+)b", "a23b\na34b", re.S)
print(arr)
编码转换
website = 'hello world'
# 按utf-8的方式编码,转成bytes
website_bytes_utf8 = website.encode(encoding="utf-8")
# 解码成string,使用utf-8的方式
website_string_utf8 = website_bytes_utf8.decode("utf-8")
生成某个时区的时间戳
根据当前时间获取时间戳
def get_now_time_stamp():
# 亚洲上海时区
tz = pytz.timezone('Asia/Shanghai')
# 系统当前时间
system_time = datetime.datetime.now(tz)
# 时间戳
timestamp = int(time.mktime(system_time.timetuple()))
return timestamp
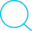
别人访问本地运行的django项目
Run browser:设置为0.0.0.0:端口号.
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:端口号
访问方式:http://本机ip:端口号
python获取文件\文件夹大小
import os
from os.path import join, getsize
def get_dir_size(dir_path):
size = 0
if os.path.isdir(dir_path):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(dir_path):
for name in files:
try:
size += getsize(join(root, name))
except Exception as e:
print('异常:', e)
# 直接用下面这句代码,在ubuntu 会出错
# size += sum([getsize(join(root,name)) for name in files])
else:
size += getsize(dir_path)
return size
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = '/home/lcx/'
file_size = get_dir_size(path)
b = 1
kb = 1024
mb = kb ** 2
gb = kb ** 3
print('There are %s %s in %s' % (file_size / b, 'b', path))
============================================================================================
import os
def look_file(path):
"""
查看文件夹下的所有文件及文件夹 join为拼接函数
"""
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path, True):
print(root) # 主目录
for item in files: # 主目录下的文件夹
print(os.path.join(root, item))
def file_dir_size(dir_path):
"""
计算文件夹 大小
"""
size = 0
# 判断是否为文件夹
if os.path.isdir(dir_path):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(dir_path, True):
size += sum([os.path.getsize(os.path.join(root, name)) for name in files])
# 目录下文件大小累加
else:
size = os.path.getsize(dir_path)
return size
if __name__ == '__main__':
path = '/home/lcx/Downloads/AxmlParserPY-0.01.zip'
file_dir_size = file_dir_size(path)
# look_file(path)
b = 1
kb = 1024
mb = kb ** 2
gb = kb ** 3
print('大小:%s b' % (file_dir_size / b))
if else
a = 1
b =2
c = 1 if a>b else 0
# 输出:0
import tkinter报错
sudo apt-get install python3-tk
gui编程,python图形界面
import tkinter as tk
import sys
import random
import re
number = random.randint(0, 1024)
running = True
num = 0
nmaxn = 1024
nminn = 0
def eBtnClose(event):
root.destroy()
def eBtnGuess(event):
global nmaxn
global nminn
global num
global running
# 修改缺陷:用户答对了,提示标签还提示信息 Edit by Hongten 2013-09-09
# 即用户在答对了以后,提示标签不应该再随着用户点击'猜'按钮而变化
if running:
val_a = int(entry_a.get())
if val_a == number:
labelqval("恭喜答对了!")
num += 1
running = False
numGuess()
elif val_a < number:
if val_a > nminn:
nminn = val_a
num += 1
label_tip_min.config(label_tip_min, text=nminn)
labelqval("小了哦")
else:
if val_a < nmaxn:
nmaxn = val_a
num += 1
label_tip_max.config(label_tip_max, text=nmaxn)
labelqval("大了哦")
else:
labelqval('你已经答对啦...')
def numGuess():
if num == 1:
labelqval('一次答对!')
elif num < 10:
labelqval('= =十次以内就答对了牛逼。。。尝试次数:' + str(num))
elif num < 50:
labelqval('还行哦尝试次数:' + str(num))
else:
labelqval('好吧。。。。。您都试了超过50次了。。。。尝试次数:' + str(num))
def labelqval(vText):
label_val_q.config(label_val_q, text=vText)
root = tk.Tk(className="比大小游戏")
root.geometry("400x90+200+200")
line_a_tip = tk.Frame(root)
label_tip_max = tk.Label(line_a_tip, text=nmaxn)
label_tip_min = tk.Label(line_a_tip, text=nminn)
label_tip_max.pack(side="top", fill="x")
label_tip_min.pack(side="bottom", fill="x")
line_a_tip.pack(side="left", fill="y")
line_question = tk.Frame(root)
label_val_q = tk.Label(line_question, width="80")
label_val_q.pack(side="left")
line_question.pack(side="top", fill="x")
line_input = tk.Frame(root)
entry_a = tk.Entry(line_input, width="40")
btnGuess = tk.Button(line_input, text="猜")
entry_a.pack(side="left")
entry_a.bind('<Return>', eBtnGuess)
btnGuess.bind('<Button-1>', eBtnGuess)
btnGuess.pack(side="left")
line_input.pack(side="top", fill="x")
line_btn = tk.Frame(root)
btnClose = tk.Button(line_btn, text="关闭")
btnClose.bind('<Button-1>', eBtnClose)
btnClose.pack(side="left")
line_btn.pack(side="top")
labelqval("请输入0到1024之间任意整数:")
entry_a.focus_set()
print(number)
root.mainloop()
获取操作者获取本机ip和外网ip
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding=utf-8
import socket
import fcntl
import struct
def get_ip_address(ifname):
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
return socket.inet_ntoa(fcntl.ioctl(s.fileno(),
0x8915, # SIOCGIFADDR
# python3.x写法
struct.pack('256s'.encode(encoding="utf-8"),
ifname[:15].encode(encoding="utf-8")))[20:24]
# python2.x写法
# struct.pack('256s', ifname[:15]))[20:24]
)
print('本机ip:', get_ip_address('lo'))
print('外网ip:', get_ip_address('eth0'))
# django中获取
x_forwarded_for = request.META.get('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR')
if x_forwarded_for:
ip = x_forwarded_for.split(',')[-1].strip()
else:
# REMOTE_ADDR要先在服务器中部署
ip = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
编译
python -c "import XXXX" # 编译XXXX
python -m compileall ./* # 同上面效果是一样的
tornado
装饰器@asynchronous装饰的handler,那么这个http请求就会成为长连接,会一直处于等待状态,直到调用self.finish(),这个请求才会结束
装饰后的函数其实已经是另外一个函数了(函数名等函数属性会发生改变)。这样有时候会对程序造成一些不便,例如想对unittest框架中的一些函数添加自定义的decorator,添加后由于函数名和函数的doc发生了改变,对测试结果有一些影响。所以,Python的functools包中提供了一个叫wraps的decorator来消除这样的副作用。写一个decorator的时候,最好在实现之前加上functools的wrap,它能保留原有函数的名称和docstring。
import functools
@functools.wraps(函数参数)
字典中有中文输出
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import print_function
import json
data = {
"test": "测试"
}
print("data: ", data)
print("json data: ", json.dumps(data, ensure_ascii=False, encoding='UTF-8'))
端口占用
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import socket
def check_port_is_alive(host, port):
"""检查端口是否存活
:rtype bool
"""
is_alive = True
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
s.connect((host, port))
s.settimeout(2)
except socket.error:
is_alive = False
finally:
s.close()
return is_alive