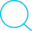
su和su -
- 联系:都是切换到root
区别
- su
- 只是切换了root身份,但Shell环境仍然是普通用户的Shell
- 切换成root用户以后,pwd一下,发现工作目录仍然是普通用户的工作目录
- su -
- 连用户和Shell环境一起切换成root身份了。只有切换了Shell环境才不会出现PATH环境变量错误。
- 切换成root用户以后,工作目录变成root的工作目录了
- 结论: 以此类推,要从当前用户切换到其它用户,应该使用su -命令。
sudo
把某些需要超级权限的运用针对性的下放,这样普通用户就不需要直到root密码,在操作时增加 sudo 即可.
查看sudo能执行哪些命令
sudo -l
sudo配置文件
- cat /etc/sudoers
#
# This file MUST be edited with the 'visudo' command as root.
#
# Please consider adding local content in /etc/sudoers.d/ instead of
# directly modifying this file.
#
# See the man page for details on how to write a sudoers file.
#
Defaults env_reset
Defaults mail_badpass
Defaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin"
# Host alias specification
# User alias specification
# Cmnd alias specification
# User privilege specification
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
hjd ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL # 所有权限都给
hjd1 ALL=/bin/more # 只给more 命令权限
# Members of the admin group may gain root privileges
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
# Allow members of group sudo to execute any command
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
# See sudoers(5) for more information on "#include" directives:
#includedir /etc/sudoers.d